SQL Server has several fixed database roles
such as
db_datareader and
db_datawriter,
which grants the user
read and write access respectively to all the tables in the database. Curiously there is no role to grant a
user permission to execute stored procedures, but fortunately this is
easily resolved by creating a new role.
The following SQL creates the new role in a database, and then grants it execute rights :
-- Create a db_executor role
CREATE ROLE db_executor
-- Grant execute rights to the new role
GRANT EXECUTE TO db_executor
A user can then be added to the new role, much like
the
db_datareader and
db_datawriter roles.
If you want to check that the role has been created and then add a user to the role, right click on a user in the
database in SQL Server Management Studio and select ‘Properties’. In the ‘Database role membership’ control
notice that the new db_executor role now appears, click the checkbox to add the user to the role, as below :
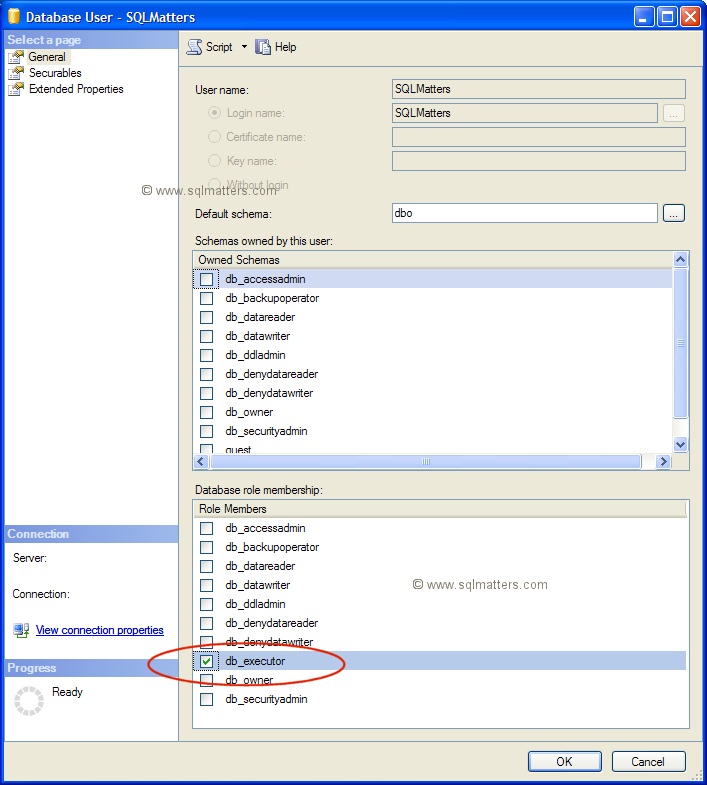
Alternatively the user can be added to the role in code using the following SQL :
-- to allocate a user to the new role :
EXEC sp_addrolemember
'db_executor','SQLMatters'
A user added to this role will be able to execute all stored procedures in the database, including
ones created in the future.
This works for SQL Server 2005 onwards.
Related Articles
The following articles may also be of interest :
Link back to this article :
https://www.sqlmatters.com/Articles/Adding a db_executor role.aspx
Keywords
SQL,permissions,user,role